By James Glanz and Stephen Farrell
New York TimesAugust 24, 2007
|
|
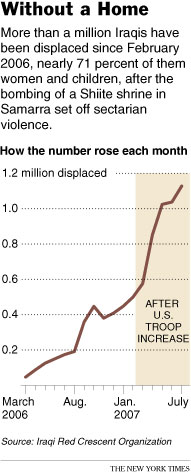
The number of Iraqis fleeing their homes has soared since the American troop increase began in February, according to data from two humanitarian groups, accelerating the partition of the country into sectarian enclaves. Despite some evidence that the troop buildup has improved security in certain areas, sectarian violence continues and American-led operations have brought new fighting, driving fearful Iraqis from their homes at much higher rates than before the tens of thousands of additional troops arrived, the studies show. The data track what are known as internally displaced Iraqis: those who have been driven from their neighborhoods and seek refuge elsewhere in the country rather than fleeing across the border. The effect of this vast migration is to drain religiously mixed areas in the center of Iraq, sending Shiite refugees toward the overwhelmingly Shiite areas to the south and Sunnis toward majority Sunni regions to the west and north. Though most displaced Iraqis say they would like to return, there is little prospect of their doing so. One Sunni Arab who had been driven out of the Baghdad neighborhood of southern Dora by Shiite snipers said she doubted that her family would ever return, buildup or no buildup. "There is no way we would go back," said the woman, 26, who gave her name only as Aswaidi. "It is a city of ghosts. The only people left there are terrorists." Statistics collected by one of the two humanitarian groups, the Iraqi Red Crescent Organization, indicate that the total number of internally displaced Iraqis has more than doubled, to 1.1 million from 499,000, since the buildup started in February. Those figures are broadly consistent with data compiled independently by an office in the United Nations that specializes in tracking wide-scale dislocations. That office, the International Organization for Migration, found that in recent months the rate of displacement in Baghdad, where the buildup is focused, had increased by as much as a factor of 20, although part of that rise could have stemmed from improved monitoring of displaced Iraqis by the government in Baghdad, the capital. |
|
The new findings suggest that while sectarian attacks have declined in some neighborhoods, the influx of troops and the intense fighting they have brought are at least partly responsible for what a report by the United Nations migration office calls the worst human displacement in Iraq's modern history. The findings also indicate that the sectarian tension the troops were meant to defuse is still intense in many places in Iraq. Sixty-three percent of the Iraqis surveyed by the United Nations said they had fled their neighborhoods because of direct threats to their lives, and more than 25 percent because they had been forcibly removed from their homes. The demographic shifts could favor those who would like to see Iraq partitioned into three semi-autonomous regions: a Shiite south and a Kurdish north sandwiching a Sunni territory. Over all, the scale of this migration has put so much strain on Iraqi governmental and relief offices that some provinces have refused to register any more displaced people, or will accept only those whose families are originally from the area. But Rafiq Tschannen, chief of the Iraq mission for the migration office, said that in many cases, the ability of extended families to absorb displaced relatives was also stretched to the breaking point. "It's a bleak picture," Mr. Tschannen said. "It is just steadily continuing in a bad direction, from bad to worse." He also cautioned that reports of people going back to their homes were overstated. As the buildup began, the Iraqi government said that it would take measures to evict squatters from houses that were not theirs and make special efforts to bring the rightful owners back. "They were reporting that people went back, but they didn't report that people left again," Mr. Tschannen said. He added that Iraqis "hear things are better, go back to collect remuneration and pick up an additional suitcase and leave again. It is not a permanent return in most cases." American officials in Baghdad did not respond to a request for comment, but the national intelligence estimate released Thursday confirmed that Iraq continues to become more segregated through internal migration. "Population displacement resulting from sectarian violence continues," it found, "imposing burdens on provincial governments and some neighboring states." Dr. Said Hakki, director of the Iraqi Red Crescent Organization, said that he had been surprised when his figures revealed that roughly 100,000 people a month were fleeing their homes during the buildup. Dr. Hakki said that he did not know why the rates were so high but added that some factors were obvious. "It's fear," he said. "Lack of services. You see, if you have a security problem, you don't need a lot to frighten people." It is clear that military operations, both by American troops and the Iraqi forces working with them as part of the buildup, have something to do with the rise in displacement, said Dana Graber Ladek, Iraq displacement specialist for the migration organization's Iraq office. "If a surge means that soldiers are on the streets patrolling to make sure there is no violence, that is one thing," Ms. Ladek said. "If a surge means military operations where there are attacks and bombings, then obviously that is going to create displacement." But Ms. Ladek added that, in contrast to the first years of the conflict, when major American offensives were a main cause of displacement, the primary driving force had changed. "Sectarian violence is the biggest driving factor — militias coming into a neighborhood and kicking all the Sunnis out, or insurgents driving all the Shias away," Ms. Ladek said. Her conclusions mirrored the experiences of Iraqis who had fled their homes. Aswaidi and her family were driven out of the Dora section of Baghdad five months ago when Shiite snipers opened fire on their Sunni neighborhood from nearby tower blocks, shooting through their windows "at all hours of day and night." Returning covertly to check on the property in mid-August, she found Sunni insurgents occupying the building and neighboring homes, walking unchallenged through the deserted streets. Nearby, she claims, the same insurgents captured one of the Shiite snipers who drove the residents away, and claimed that he was a 16-year-old Iranian. She now fears that her entire neighborhood will be taken over by Shiite militias like the Mahdi Army, which is loyal to the radical Shiite cleric Moktada al-Sadr. "I don't want them to take my town, but I think they will," Aswaidi said. "It will change from Sunni to Shia. The Americans can't stop it." Shiites face similarly overwhelming odds. In Shualah, on the northern outskirts of Baghdad, 400 Shiite families now live in a makeshift refugee camp on wasteland commandeered by Mr. Sadr's followers. In a sprawl of cinder block hovels and tin and bamboo-roofed shacks, families have stories of being expelled from their homes by Sunni insurgents. Ali Edan fled Yusifiya, a Sunni insurgent haven south of Baghdad, when his uncle was killed. He has no intention of returning, even though American commanders claim Sunni sheiks there have begun cooperating with them. "It is still an unsafe area," said Mr. Edan. Both humanitarian groups based their conclusions on information collected from the displaced Iraqis inside the country. The Red Crescent counted only displaced Iraqis who receive relief supplies, and the United Nations relied on data from an Iraqi ministry that closely tracks Iraqis who leave their homes and register for government services elsewhere. Before the troop buildup, by far the most significant event causing the displacement of Iraqis was the bombing of a revered Shiite mosque in Samarra in February 2006. The bombing set off a spasm of sectarian killing, but the rate at which Iraqis left their homes leveled off toward the end of that year before accelerating again as the buildup began, the Red Crescent figures show. The United Nations figures also include a little over a million people it says were displaced in the decades before the Samarra bombing, including the Iran-Iraq war of the 1980s. The Red Crescent data does not include them. In Baghdad, the latest migration involves an enormously complex landscape in which some people flee one district even as others return to it. In Ghazaliya, a mixed but Sunni-majority district of north Baghdad, one 30-year-old Shiite said his family was driven out by Sunni insurgents a year ago with just two hours notice to leave their home. Five months ago, the troop buildup brought American soldiers and the Shiite-dominated Iraqi Army onto his street and his family returned. But even as it did, Sunni neighbors fled, knowing that the army had been infiltrated by Shiite militias. "They are afraid, because the army has good relations with the Mahdi Army," said the 30-year-old man, who said he was too afraid to give his name. "My area used to have a lot of Sunni. Now most are Shia, because Shias expelled from other places have moved into the empty Sunni homes." |
|